Generating a new SSH key
This guide describes how to generate and use a private/public key pair to log in to a remote system with SSH using PuTTY. PuTTY is an SSH client that. Although the SSH protocol is considered secured as the traffic is always encrypted, it. Key based authentication works with a pair of public and private. What is SSH key-based authentication? A review of SSH authentication methods with its advantages and disadvantages. A description of key creation and connection to a remote server in Windows.
- Find out how to protect your server's sensitive data by learning how SSH keys work, creating an SSH key pair, and creating FTP users in SiteWorx. Hosted private cloud on enterprise hardware, powered by VMware & NetApp. Server Clusters. Multi-server configurations for maximum uptime & performance.
- A tutorial on configuring SSH Server to Authenticate with Private/Public Keys using Ubuntu Linux http://www.danscourses.com/Linux-Fundamentals/how-to-install-ssh-in-ubuntu-388.html.
- Open Git Bash.
- Paste the text below, substituting in your GitHub email address.
This creates a new ssh key, using the provided email as a label.
- When you’re prompted to «Enter a file in which to save the key,» press Enter. This accepts the default file location.
- At the prompt, type a secure passphrase. For more information, see «Working with SSH key passphrases».
Adding your SSH key to the ssh-agent
Before adding a new SSH key to the ssh-agent to manage your keys, you should have checked for existing SSH keys and generated a new SSH key.
If you have GitHub Desktop installed, you can use it to clone repositories and not deal with SSH keys.
- Ensure the ssh-agent is running. You can use the «Auto-launching the ssh-agent» instructions in «Working with SSH key passphrases«, or start it manually:
- Add your SSH private key to the ssh-agent. If you created your key with a different name, or if you are adding an existing key that has a different name, replace id_rsa in the command with the name of your private key file.
- Add the SSH key to your GitHub account.
This tutorial explains the Passwordless SSH using Public Key and Private Key in Linux.
SSH stands for Secure SHELL, is a protocol used to connect remote hosts to login or performing some tasks using scripts.
When we want to automate some tasks on remote hosts using scripts from a centralized server like Jenkins/Ansible or any Linux Server, we may require a password less connection between the remote hosts and the centralized Server.
In this tutorial, we will learn to create Passwordless SSH login using public key and private key. Follow the step by step guide to make your ssh connection passwordless.
This tutorial will work for Linux Destro such as Centos, Ubuntu, Redhat, Amazon Linux(AWS EC2) and Other as well.
Recommended Read:How to Install Jenkins on Ubuntu
Also Read : Git Tutorial for beginners (Part I)
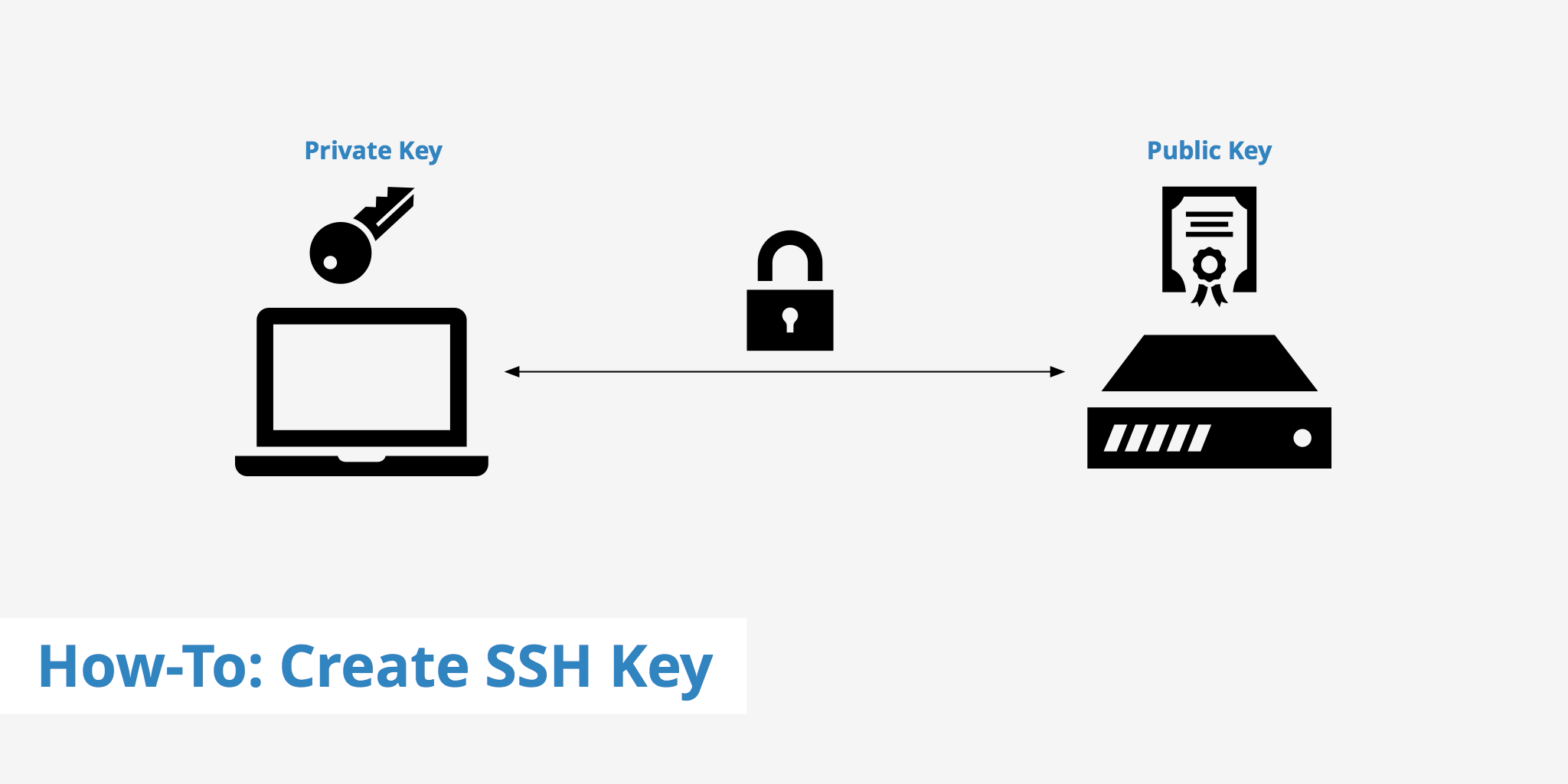
Scenario
We have one Local Machine and one Remote Server.We will setup a passwordless connection to login Remote Server from the local Machine.
Perform following steps on the remote Server
Step 1– Create an User and login or login as an existing user.
$ useradd devops
$ su – devops
Step 2 – Generate a key pair ( Public key and Private Key) using ssh-keygen command.
Before running this command make sure you are on home directory of the user.If not you can go to the home directory by cd ~ command.
$ cd ~
$ ssh-keygen -t rsa
It will ask for some details. Do not put anything here and press ENTER only.
By ls -al command you can see a hidden directory .ssh and two files namely id_rsa and id_rsa.pub inside .ssh directory are created.Here id_rsa is the Private key and id_rsa.pub is the Public Key.
Private key(id_rsa) is kept at source computer(local machine) from where you have to ssh. Public Key(id_rsa) is kept at Destination Server(Remote Server) , the Server you want to access.
Step 3- Create a file name authorized_keys in side .ssh directory and copy the content of id_rsa.pub file to authorized_keys file.
Go to .ssh directory
$ cd ~/.ssh/
Create an empty file name authorized_keys
$ touch authorized_keys
Copy the content of id_rsa.pub to authorized_keys
$ cat id_rsa.pub > authorized_keys
Check the authorized_keys file if contents are copied.
$cat authorized_keys
Step 4 – Change the permission of authorized_keys
$ chmod 600 authorized_keys
Ssh Private Key Linux
Step 5– Copy the content of id_rsa file
Use cat command to display the content of id_rsa and copy its content.
Ssh With Private Key Path
$ cat id_rsa
On the local Machine
Step 1– Create a file and paste the content of id_rsa copied from remote server inside this file. You can use nano command to perform this action.
Create a file name devops.key using nano command , paste the content and pres Ctrl+X to save and close the file.
$ nano devopys.key
Step 2 – SSH remote Server from local machine without using password.
$ sudo ssh -i path-to-private-key [email protected]
$ sudo ssh -i devops.key [email protected]
I hope you enjoyed this tutorial and learned Passwordless SSH login using public key and private key. If you think this is really helpful, please do share this to other as well. Please also share your valuable feedback, comment or any query in the comment box.I will really happy to resolve your all queries.
Thank You
If you think we helped you or just want to support us, please consider these:-
Connect to us: Facebook | Twitter
